In this lesson we will take a deep look at Google’s ranking algorithm and discuss over 200 features and factors that are known and believed to play a role in creating Google’s organic search rankings. Before we do there are three points that must be kept in mind.
- First and foremost, Google closely guards their actual algorithm, so this information is not taken directly from Google. This information was compiled from numerous studies and surveys of SEO professionals who spend their careers reverse engineering Google’s rankings to determine what factors play a role in the Algorithm.
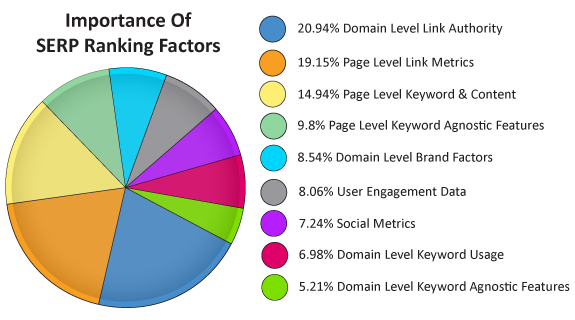
- It is estimated that there are over 200 factors in Google’s algorithm and each of them is weighted differently. While some factors play a larger role than others, none of these factors can significantly “move the needle” by itself. In order to rank well in Google you should attempt to align your website, it’s content and marketing strategies with as many of these factors as possible.
- Google has stated that they make hundreds of adjustments to their algorithm every year. Here is a good way to think about it. If you have ever seen the inside of a recording studio, you may have seen a sound technician standing over a huge sound board with lots of different knobs, switches and sliding levers. Google’s algorithm is sort of like that soundboard and Google’s engineers are like the sound technician, constantly adjusting each equation in their algorithm to achieve the best results possible. So, whatever the exact algorithm is today, it will change in the future. However, if you understand the majority of factors and Google’s philosophy, you will be well prepared to remain relevant and dominant in your niche well into the future.
With that said, the following 210 factors are either known or strongly believed to play a role in Google’s organic ranking algorithm. These factors have been identified through large scale surveys of SEO professionals as well as through extensive testing and analysis across thousands of websites. Get these things right, and your site will do very well in Google search results.
Lastly, the second half of the Google Strategy Workbook is meant to be used in conjunction with this lesson on Google's ranking algorithm. Open the workbook and enter notes and answers as you move through this lesson. If you do that, by the end of this lesson you will have an incredible list of actionable items that will lead you toward a highly optimized website.
This group of Domain factors are relevant to your root domain name. These considerations will give you some insight into what effect the actual root domain of your website can influence your site’s ability to rank in Google.
1: Domain Age Many of the equations in Google’s ranking algorithm look at the performance of a website in a specific, over time. Domain age establishes a history for a website. A site that has established itself as a consistent provider of content related to a specific niche over a long period of time will have an advantage over a site that is brand new to that niche. This can negatively effect a site for the first year or so that it is live. However, Matt Cutts has said that it is not that big of a factor and the negative aspects of a brand new domain are more likely due to a lack of other things like content, links and mentions from around the web. Those things take time to build up.
2: Keyword Use in Top Level Domain Using a keyword in a domain name used to give that site a significant boost in the rankings for that specific keyword. However, recently Google has diminished the importance of this factor. It can still provide a boost for that term, but it is no longer as important as it once was. Still, the use of a keyword gives Google an idea of what that site may be relevant to. For instance a website called “WhiteTeethDentistry.com” is likely to be about dentistry. So this can still provide Google a valuable clue in how they should categorize that site.
3: Keyword As First Word In Domain When it comes to keyword strategies, the idea of “prominence” is a recurring theme. Basically, the verbiage that you use at the beginning of something is likely to set the tone for that content. Therefore, particular consideration is given to the words that appear at the beginning of content, page titles, descriptions and URLs. So, if your domain name starts with an important keyword, this can give you a slight edge in ranking for that term. However, as mentioned in the previous factor, Google has diminished the significance of this factor. It’s still believed to be a factor… but a small one.
4: Subdomains For a long time Google considered sub-domains as completely separate from their root domain. Essentially a sub-domain was known to be related to its root domain, however the content relevance and link equity from a sub-domain would not help your root domain rank better. However, in 2011 Google changed its stance on subdomains and began considering links to a sub-domain the same as a link to the root domain in terms of a site level ranking factor.
5: Keyword in Subdomain Name Subdomains are often used by websites and web portals to house various niche content. This factor is highly related to the above two factors in that using a keyword at the beginning of a sub-domain can give Google an indicator as to what that specific sub-domain is relevant to. In surveys, SEO professionals agree that this has traditionally provided a boost in rankings for some keywords.
6: Domain Registration Length Much of Google’s algorithm is about determining the trustworthiness of a site because their organic search rankings can be seen as a recommendation to their users. Sites that have a domain name that is set to expire in the near future may not be as legitimate and trust worthy as sites that are registered long term. Google has a patent that actually speaks to this line of reasoning.
7: Domain History A site with a history of numerous changes in ownership (verifiable through whois) may indicate problems with reliability and trust and Google may decide to “reset” the history of that site, thus negating the benefit of any links pointing to that site. Whether Google does this is wholly up to Google, therefore if you are considering purchasing a site that has a negative history, you should not count on this Google reset. Actions may be necessary to “clean up” any mistakes, such as spammy practices from the past.
8: Exact Match Domain Exact match domains used to provide a very powerful edge in Google’s organic rankings. However, in 2012 Google introduced the EMD (exact match domain) update to their algorithm and effectively diminished the importance of this factor. However, it is believed that exact match domain can still provide a slight edge in ranking for the exact match keyword phrase if the site is a legitimate and quality site. For low quality sites, a penalty has been introduced to ensure that the search results are not being unfairly manipulated.
9: Public vs. Private WhoIs Hiding the information about who owns a website is a red flag for Google. By itself it may not cause any negative actions or penalties, however when that is seen in conjunction with a few other red flags, an algorithmic penalty could be introduced. While this may just be about protecting the personal information of the site owner. Google sees it as potentially having something to hide. Take note: Google likes websites to offer a high degree of transparency… sites other than Google of course.
10: Penalized WhoIs Owner If Google is able to identify a particular person as a repeat offender or “spammer” then a penalty could be automatically placed on other sites owned by the same person.
11: Country TLD Extension Use of a Country Code Top Level Domain (such as .in, .ca, .co, .uk, .cn, etc…) can help that site rank within that country or region, however it may also affect the site’s ability to rank universally.
This is a group of factors that apply specifically to an individual webpage. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies that deliver what these factors are looking for, will help your site will be able to dominate search rankings for your target terms.
12: Keyword in URL The specific words used in the URL provide relevancy signals, therefore keyword use can help the page rank for those keywords.
13: URL Length Excessively long URLs may be difficult for search engine spiders to crawl and thus pages with extremely long URLs may find it difficult to achieve top rankings.
14: Dynamic URLs Dynamic URLs (those that include a =? with a bunch of jumbled up letters, numbers and special characters) immediately tell a search engine that the page is dynamically pulling all of its content from a database. There are two problems here. First, Google cannot be sure that a page that is dynamically generated will provide the same information each time it loads, and therefore they cannot be sure what users will see if they click on your link from a SERP. Also, dynamic URLs are missing out on a great opportunity to give Google relevancy clues through the use of keywords and categories in the URL structure. Dynamic URLs are bad and should be avoided.
15: URL Path The URL path can send signals to search engines about how that content should be categorized. Therefore keywords along the URL path can help the page rank for thematic keywords. Also, pages that are closer to the homepage could get an authority boost. If you consider the URL structure as an indicator of the hierarchy of the site and page that sit above a lineage of many supporting pages will appear to be more fundamentally important to your site and thus can find it easier to achieve good search rankings.
16: Page Category The category that a page appears in is a clear relevancy signal to Google. Essentially, Google seeks to categorize information and how you choose to categorize information on your site gives Google a strong indicator of how that information should be categorized. This is why a flat URL structure where every page on a site sits directly under the homepage is missing a critical opportunity.
17: Rel=”Canonical” This tag helps Google understand which page is supposed to get the credit and rankings when there are instances of duplicate content.
18: Keyword In Meta Title Tag The title tag of a webpage is one of the most important on-page factors. The title tag is what will appear as the blue link in Google’s search engine result pages (SERPs). Also, just like the headline for a story often gives a clue to what the content of the story will be about, so too does the title of a page indicate what that page is relevant to. The title tag has a maximum limit of 512 pixels based on the font Google uses in their search results. On average this equates to 57 characters but that varies depending on the width of the characters used in the title. If you go beyond the pixel limit, Google is more likely to create and display their own title for your page. The idea of keyword prominence may play a role in the title tag, meaning that it could be slightly better to start your title tag with the most important keyword for the page, however, what is more important is that the keyword is used and that the title tag is well written and engaging to potential users.
19: Keyword Use In Description Tag The content of the description tag is another highly important on-page SEO factor. If formatted properly, the description tag is what Google will use under the blue title link in their SERPs. Use of your target keyword in your description tag gives Google another strong indicator about what the content your page is relevant to. It should be noted that the description tag has a limit of 160 characters. While search engines will index up to 255 characters, 160 characters is the limit for what Google will display in their SERPs and if you go beyond that limit they are more likely to create their own description for your page.
20: Semantic Clues In Title and Description Tags The use of semantic indicators within titles and descriptions can give powerful signals to Google that your page is not just optimizing for the one target keyword, but is actually providing a well rounded discussion of the subject matter.
21: Keyword In H1 Tag The H1 tag is typically used to display the title of the content of that page to visitors when they are actually viewing the page because an H1 tag typically makes the content within the tag appear the biggest and boldest content on the page. H1’s typically appear at the top of the content in a headline and thus provide a strong indicator as to what the page is about. Using a keyword in your H1 can send a strong signal to search engines and boost rankings for that term. There should only be one H1 tag used per webpage.
22: Keyword in H2-H6 Tags Much like the H1 tends to set the stage for the entire page, sub-headings set the stage for various sections within the page. When your keyword and thematic keyword variations appear in sub-headings it demonstrates to Google that you are exploring various aspects of the target topic. It is perfectly acceptable to use multiple H2-H6 tags per webpage.
23: Keyword Word Order A page that is optimized for a specific phrase will tend to rank better for that exact match phrase compared to variations of that phrase. For instance, if someone searches for “best IPA microbrews”, then a page that is optimized for “top IPA microbrews” will tend to rank better than a page that is optimized for “microbrews best IPA”.
24: Keyword Prominence It is important to use target keywords and phrases close to the beginning of content as that tends to set the stage for the exploration of that subject matter. If a word doesn’t appear until the middle of a page, then that page is probably not very focused on that specific word… but if the word appears at the beginning, middle and end, then that page seems to have been discussing that word more thoroughly.
25: Keyword Density / Keyword Is Most Frequently Used Phrase In Document This was actually the most important factor and the basis for the earliest search engine algorithms. Search engines can quickly create a list of all the words and phrases used on a page, and determine how many times each of those words and phrases are used throughout the page. This gives a keyword density.
For instance, if you have a one word keyword, and the document has a total word count of 100 words, and you use your keyword 5 times throughout the document, then you would have a 5% keyword density for that keyword.
However, if you were using a 3 word keyword phrase, and that phrase appeared three times on a page that had 100 total words, then you would have a 9% keyword density for that phrase.
Keyword density sends a signal to search engines as to what is the focus of the content on that page. The ideal keyword density changes based on the total word count. For instance, if you have a page with 400-600 words, then a 3-5% keyword density is ideal for your target keyword phrase. If you only had a .5% keyword density, then the page would not appear to be strongly focused on that term, and if you had a 15% keyword density then it would appear that you have just stuffed that keyword into the content an inappropriate amount of times (a spam tactic that can trigger a penalty). Also, if you have 800-1,200 words on the page, then a 5% keyword density may be too high.
26: Content Length Content length can provide search engines a way to gauge how well that page covers a topic. If a page only offers 100-200 words on a topic, it is not likely to be as important or relevant as a page that offers a 900 word discussion on the same topic. Recent studies have shown that Google gives a strong preference (in terms of top rankings) to pages with 800-1,000 words of content. At the same time, pages with low word count compared to similar pages on other websites may be deemed "thin content" and draw a Panda related penalty.
27: Depth of Exploration of Subject Matter When Google engineers set out to determine how recognize “high quality content” they first had to define it and they came up with a list of questions and ways of looking at a topic that were typically associated with high quality content. What they came up with was a list of ways to explore any given subject matter that are encyclopedic in their depth and breadth. Therefore, an encyclopedic exploration of subject matter can help your page rank more highly.
28: Useful Content Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines state that Google places different types of searches into different “buckets”. This is how Google decides which types of search results features to return to the user. Google will therefore categorize some content as useful, rather than just informational. For instance, a loan calculator is more useful to an end user than just a link to a company that offers loans and that type of useful content may help a page rank higher for thematically relevant terms.
29: Helpful Supplementary Content According to a leaked Google Quality Rater Guidelines document, when a page offers links to supplementary content that explores the topic in a variety of ways that are relevant to the topic of the page, those supplementary pages are adding relevant value and adding to the quality of the page. Therefore, it is very important to think of content in terms of topics with nested pages that explore every niche relevant to the subject matter.
30: Use of Bold and Italic on Keywords in Content The use of mark-up that will draw some kind of emphasis to those words. For instance, words written in bold on a page are usually express added significance and importance to the overall subject matter of the page. Therefore, using text mark-up such as Bold and Italics on target keywords can help the page seem more relevant for those specific keywords.
31: Hidden Text / Expandable Divs Having more content on a page allows that page to have a higher word count, gives you more opportunities to explore the content in a variety of ways, and ultimately can be more likely to give users the information they are looking for. However, you may not always want all of that content to show when the page loads. However, hiding content through the use of CSS is a signal to Google that you may be using a spammy strategy to game the system and that could get your page penalized. One good way to accomplish the hiding of text is to place that text within an expandable div. This can be a good strategy if implemented correctly. First, it must be obvious to the user that the additional text is there. To do that you should display at least some teaser of the information and include a clear button or link such as “Read More” that clearly tells the reader that more information can be found by clicking it. Second, you should use JavaScript to fire the CSS that is actually hiding the text. This is because Google does not process JavaScript, therefore Google will ignore the JavaScript and simply give your page full credit for the content.
32: Latent Semantic Indexing of Keywords In Content Google is getting closer and closer to truly understanding human language and context is an important part of this. Because words can often have different meanings (eg: Apple Computer vs. Apple the fruit), it is the use of context and related terms that help Google with the formal semantics which are the logical aspects of meaning such as sense, reference, implication and logical form, and lexical semantics which is about word meanings and word relationships. Google’s hope is to move toward conceptual semantics which will help them determine the cognitive structure of meaning. To put it in simple terms, you want to use synonyms, antonyms and a variety of interrelated discussion points to demonstrate to Google that you are providing a well rounded and thorough exploration of the subject matter.
33: Duplicate Content Identical content on multiple pages within the same site presents a number of problems. First, it is confusion to Google about which page should rank for that content. Also, when other websites choose to link to that content those links could get spread thin across several version of the same content. Both of these scenarios can negatively influence your rankings.
Another duplicate content problem is when your site features content that is identical to that of other pages throughout the web. Google seeks to reward the creators of original content and the Panda update introduced penalties for this type of duplicate content in a effort to push aggregators down the rankings and help content originators get the rankings and traffic they deserve.
34: Multimedia Google seeks to give priority rankings to sites that offer the most thorough and high quality exploration of the subject matter related to the keyword being searched. A page that offers multiple types of content including written, images, video, audio, etc… takes advantage of sending additional signals to Google. However, the content must be marked up correctly.
35: Image Optimization Optimized images can definitely help a page rank better for targeted search terms while also giving the page additional types of searches that it can rank for (Google image search). Image file names and image alt tags should be used strategically to demonstrate relevance to the desired keywords. Also, Google is making incredible strides in being able to identify places, objects and people in images. Upload a picture in Google Image search and Google will return a list of remarkably similar images, an often the exact same image. Therefore, if your images have simply been downloaded from a stock image site, do not expect an SEO boost. However, completely original images can provide a nice SEO boost. Still, use keyword rich file names, Schema.org mark-up, image alt tags, and an image sitemap to ensure maximum SEO value.
36: Grammar And Spelling Proper grammar and spelling is a quality signal. Pages that feature content with mistakes in either spelling or grammar could indicate that the content is low quality and would not offer a good user experience. Ensuring that your content is free of these types of errors will send signals to search engines that you have high quality content as well as provide a high quality user experience.
37: Aggregated & Syndicated Content A major focus of Google’s Panda Update was to push sites that feature aggregated / syndicated content down the search results and to help sites that feature high quality original content rank highly. If your site features syndicated content it is important that your site is adding significant value in some way. Sites that do a god job of curating high quality content and adding value will be able to rank. Added value is the key.
38: Tags Tags are a way to categorize content and therefore indicate a topical relationship between content. Also, the keyword of the tag being used is a relevance signal for categorization.
39: References and Sources Similar to citations in research papers, providing citation references and information sources is a signal of quality as well as relevance. The Google Quality Rater Guidelines tell reviewers to look for sources when looking at certain types of pages when expertise and authoritative sources are important.
40: Bullets and Numbered Lists Bullets and numbered lists are attractive to readers because they help break up content, generally making it easier to read and understand the points that are being presented. Therefore Google may reward content that provides bullet points and numbered lists.
41: Reading Level It is speculated that Google takes the reading level of a page into consideration, however there is conflicting schools of thought about how to optimize reading level. A very basic reading level could appeal to a broader audience, however a higher reading level could indicate a higher quality page. In general, you should create content that will best cater to the audience that you are marketing to and create content at a reading level that is most appropriate to the subject matter.
42: Reviews & User Generated Content Reviews & User Generated Content on a page give Google a very clear understanding of the quality of user experience from that page. Pages with lots of comments that are on topic and add to the discussion of the subject matter, and pages with good product or service reviews, will tend to perform well in the SERPs. However, this general rule of thumb has been closely scrutinized by Google and a new level of attention is being paid to the quality of the content in user generated content as well as the authority of the people taking part in the conversation. Google sees low quality discussions for what they are. For instance a Q&A page that features only a question and no answer is considered low quality. However, a Q&A page that features a lot of answers that are either not relevant or useful is also low quality. User generated content is great as long as it is on topic and furthering an insightful and high quality discussion of the topic.
43: Recency of Content Updates Google’s Caffeine Update introduced a factor that looks at the freshness of content, meaning when content is provided and updated. Google seeks to reward sites that are remaining current and actively participating in the web. Some SERPs will contain the date stamp showing when a page was last updated which is a give-away that this is a ranking factor.
44: Magnitude of Content Updates The significance of changes to content is also taken into consideration as updated to entire sections may be more important than simply changing a few keywords.
45: History of Page Updates The frequency of page updates also plays a role in the freshness of the page. When content is updated it can mean that the content has changed and the content may or may not be deserving of the same rankings as before. Therefore, a page that significantly updates it’s content very often may be less trustworthy, or it may be more trustworthy depending on the subject matter of the page. This is an area where the history of updates and how they either positively or negatively affect a page is highly related to semantic indexing factors. For instance a page that regularly updates stock quotes, news stories or real estate information will receive a freshness boost, whereas a small business homepage that is constantly changing it’s product and service descriptions may indicate trust issues.
46: Quality of Other Keywords The Page Ranks For If the page ranks for other keywords it may give Google an internal sign of quality. Therefore it could benefit a page to first try to rank for easier, long tail terms before going after higher search volume more general terms.
47: PageRank of The Page PageRank is measured on a scale from 1-10 and is the result of a page specific Google algorithm that quantifies the link juice for that page. While PageRank itself is not a complete picture of the authority of a page, higher PageRank tends to correlate to higher search rankings.
48: Quantity of External Links Pointing To A Page The first and easiest measure of the backlink profile for any webpage is the number of links pointing to the page. A page with more links pointing to it will tend to outrank a page with fewer links pointing to it.
49: Quality of External Links Pointing To A Page More important than the quantity of links pointing to a page is the quality of those links. All of the algorithmic metrics that apply to your page, also apply to every page that is linking to you. Getting a link from a page that is of high quality, on a trusted site, with high quality content that is relevant to the content of your page, will make that page a stronger link partner. When it comes to linking, quality is more important than quantity, although both are taken into consideration.
50: Quantity and Quality of Traffic Sent By Links To Your Page Recently Google has begun placing increased importance on links that actually get clicks and drive traffic to your site, over links that do not drive traffic. Therefore, a link from a less authoritative site that actually drive traffic to your site can be better than links form a highly authoritative site that do not actually drive traffic. Google is also taking into consideration user experience metrics such as whether those links are associated with a high bounce rate. These factors can increase or decrease the quality of individual links.
51: Quantity of Internal Links Pointing To A Page The number of internal links to a page indicates the importance of that page relative to other pages on the site. For instance, every page within the site will typically link to the homepage, and therefore the homepage is typically seen as the most important page on the site.
52: Quality of Internal Links Pointing To A Page Internal links from pages within your site that are more important, such as top level category pages, will have a more powerful effect than less important pages such as deep content with less PageRank.
53: Number of Outbound Links PageRank flows to and from webpages though links. Just as inbound links give a page “link juice”, outbound links allow “link juice” to flow out from that page. While a few highly thematic and relevant outbound links could improve a pages ability to rank, too many outbound links could potentially hurt search rankings. As a general rule of thumb a page should not have more than 100 outlinks including navigation and advertising.
54: Outbound Link Quality Linking out to high quality pages that are highly relevant to the target subject matter of the page will actually help the page rank for its target terms. This is true whether the links point to on-site supplementary resources or off-site resources. Essentially, Google’s goal is to help people find what they are looking for, if your page offers curated links to additional resources on that subject matter, then it could be beneficial to the end user in their quest for information and thus Google could look favorably on such a strategy. The Google Quality Rater guidelines for 2014 specifically place increased emphasis on pages with links to relevant supplementary content as a factor that increases the quality of a page.
55: Outbound Link Theme The pages that your page links to could send search engines signals about the subject matter that your page is relevant to. For instance if your page provides a curated set of links about microbrew beer making techniques, then it could indicate to Google that your page is a good resource for people who are interested in microbrew making techniques.
56: Affiliate Links Affiliate links and participation in affiliate marketing strategies is perfectly fine, however if your page features any advertising links more prominently than the content of the page, then you could be in danger of Google classifying your page as a “thin affiliate” page and this could negatively impact your search rankings.
57: Broken Links A page with numerous broken links is a sign of a neglected page that will offer a lower quality experience to visitors. Therefore, broken links will tend to diminish a page’s ability to rank well in Google.
58: User Friendly Page Layout The Google Quality Rater Guidelines state: “the page layout on the highest quality pages makes the main content immediately visible.” Also, Google’s Page Layout update clearly introduced penalties for pages that feature “too much” advertising above the fold. Essentially, users visit a page for its content, and Google rewards page that make content the top priority.
59: Page Host’s Domain Authority The higher your domain authority, the easier it will be for any page you put up to quickly achieve top rankings. If two web pages are identical in terms of quality of content, links, etc… the page that is hosted on a domain with higher domain authority will rank higher than the page on the domain with a lower domain authority.
60: Page Loading Speed Both Google and Bing use page loading speed as a ranking factor. Search engines have a vested interest in recommending websites to their users that will provide a good experience. It has been shown in study after study that sites that load fast have better engagement rates, whereas sites that load slowly have higher bounce rates. This is particularly true for mobile users. Therefore, Google and Bing will reward sites that load fast with better rankings.
61: Priority of a Page in XML Sitemap One of the elements for each page in an XML Sitemap is the priority of that page. Priority is ranked by tenths from 0.0-1.0. Typically your homepage should be a 1, top level category pages that appear immediately under the homepage should be a .9, sub-category pages should be a .8, and so on following the URL index structure of your site. However, some pages such as About Us or Policy pages that may appear directly under the homepage may be a lower priority such as a .5. While the URL index structure method for ranking pages is a decent rule of thumb, the page priority is a signal to search engines about how important you feel that a particular page is to your site and the user experience.
62: Page Age There are two somewhat conflicting portions of Google’s algorithm at play here. Google’s caffeine update sought to help fresh and relevant content rank more quickly so that current events and the most up to date information could be more easily found by users. Still, an older page that is updated regularly may outperform a newer page, however this may also simply be due to an older page having build up a more significant profile of off-site quality indicators such as links and mentions, and may have a history of user engagement signals such as clicks, low-bounce rate, time on site and conversions that would clearly indicate quality and those signals come with time.
63: Human Editors / The Google Quality Rater Program Google does utilize human editors in some cases. For instance in the case of application of manual penalties, human editors at Google have made the decision to apply a specific penalty to a page or even possibly an entire website. Conversely, it is believed that in some instanced Google can decide to allow human editors to push some pages higher in the rankings, although this has never been officially confirmed.
64: Parked Domains In December 2011, Google introduced an update that decreased the search visibility for parked domains. Some sites have used link schemes that include links from a lot of parked domains. This link scheme can now result in penalties.
The following group of factors are technical factors associated with the presentation of code for each individual page on your site.
65: Schema.org Structured Data Microformats Schema.org structured data microformats are sets of tags that can be added to the code of your page to help every different field of content on your page be identified as its own entity. These tags tell search engines to classify content as an article, blog, person, business, event, product, image, video and much more. More and more Google is moving toward its knowledge graph being the brain and central nervous system of all of its various offerings. Schema.org structured data microformats are what knowledge graph uses to better understand and relate all digital information.
66: HTML & CSS Errors / Validation Lots of HTML and/or CSS errors are a sign of a low quality site that could have user experience problems. Similar to the need to minimize spelling and grammatical errors, coding errors should be avoided. Use the W3C HTML and CSS validators to verify the code quality of your pages.
67: Where Your Body Content Appears In Source Code There are numerous best practices in the organization and presentation of the source code on your pages that are often associated with sites that rank better. For instance, the higher up in your source code that the main content for your page appears, the better. Google wants to see that your content is featured prominently on your page. Therefore, if the main body content of your page does not appear until after all of the navigation, sidebar content and advertising, then it would stand to reason that your main body content isn’t really the star of the page. By placing your main body content as close to the top of your code as possible, it will appear more important to the page.
68: In line CSS and/or Javascript or Excessive File Loading This is an indirect factor because the more script that search engines have to index and browsers have to render, the more bandwidth and longer amount of time it takes for your page to load. These factors can send poor user experience signals. CSS & Javascript should be minified (meaning any non essential characters or spaces should be deleted) and combined into external files. While many popular CMS systems that use plug-ins and modules will add numerous separate CSS and JavaScript files to pages throughout the site, the number of these external files should be minimized whenever possible. So, combine, minify and externalized CSS and Javascript.
69: Order of Code Sites that streamline their code to optimize loading time and minimize the use of browser and server resources seem to perform better in search engines. By presenting clean code that places HTML and CSS before Javascript your page will perform better in SERPs.
70: Robots Index Follow Adding this meta tag:
<meta name=”robots” content=”index, follow”>
to the head section of your webpages offers instructions to search engine robots that you want them to index the page and follow any links that appear on that page. Conversely tells robots to not index the page and not to follow the links that appear on that page. Additional combinations of “noindex, follow” and “index, nofollow” offer instructions as to whether the page should be indexed and the links should be followed. Google has note that it spiders will follow these instructions most of the time.
71: Robots.txt A robots.txt file provides instructions to search engines about which files not to crawl, index or cache on its servers. Google is on record as claiming to follow the instructions given to its robots in the robots.txt file. Therefore, if you have pages or sections of your site that you do not want Google to crawl, index and cache on its servers, then listing those pages in your robots.txt file can provide your solution. Pages that you list in your Robots.txt file with instructions to nofollow, noindex those pages will effectively eliminate those pages from Googles SERPs. However, it is widely believed that Google will still crawl any pages that it can access and will simply place a filter on those cached pages on it’s servers.
Each of the following factors can have a site-wide effect on your rankings.
72: Content Generally Provides Unique Insights and Added Value Google has stated that sites that do not bring anything new to the table will not rank highly in search results, especially “thin affiliate sites”. Google is actively seeking to reward the creators of unique and original high quality content. Therefore, in order to rank highly a site should deliver added value compared to other similar sites that already exist. This factor certainly applies to individual pages, however it is also believed that the history of your site as it relates to this area can affect your overall site quality score.
73: Contact Us Page & Return and Exchange Policies for Ecommerce Sites The Google Quality Rater Guidelines state that they prefer sites that provide easily accessible contact information. It is believed that there is an additional bonus when the contact information matches the WhoIs information. For Ecommerce sites that easy to find return and exchange policies are trust indicators.
74: Domain Trust / TrustRank Just like PageRank is measured by the links that a page has pointing to it, TrustRank is a metric that measures the quality of sites that link to you and that you link out to. Associations with high quality sites are a quality signal that indicates trustworthiness. This may be one of the most important factors in a sites ability to rank highly for relevant keywords.
75: Site Architecture A site architecture that creates thematic silos of content relevance helps Google thematically categorize your content and can therefore provide a profound boost to SEO. Google prefers content to be grouped around a topic with an overview being supported by supplemental content pages that provide depth and breadth on various aspects of the subject matter.
76: Site Updates How often a site is updated, especially with new content, gives Google signals of freshness and indicates that the business is an active participant in the web and is more likely to actively take care of their users.
77: Number of Pages A site with a low number of pages is a sign of weak authority compared to a site with a high number of pages.
78: Presence of an XML Sitemap An XML sitemap helps search engines find and index all of the pages on your site more thoroughly. A properly formatted sitemap will also give search engines information about the importance of each page, when the page was last updated and how often the search engine should come back to index each page.
79: Site Uptime Sites with lots of downtime from site maintenance or server issues tell search engines that your site may not be trustworthy, which may hurt your rankings and cause the site to be deindexed if not corrected.
80: Server Location Server location can affect a sites ability to rank well within a geographic region. For instance, in sites that seek to improve international SEO, hosting locally within that country or region could help improve rankings within that country or region.
81: SSL Certificates Google has confirmed that they index SSL Certificates and in an effort to make the web more secure Google has come out and stated that SSL certificates have been added as a ranking factor. Therefore, sites with SSL certificates will tend to outrank Ecommerce sites that do not have SSL Certificates. Of course, there are many other factors that can certainly outweigh this one factor... but it has been definitively identified as contributing factor and therefore every site should begin using SSL.
82: Terms of Service and Privacy Pages These two pages are expected from a site that is a trustworthy member of the Internet. These are basic and standard pages that every site should have and can help improve rankings.
83: Duplicate Content On-Site Duplicate pages, meaning duplicate content, meta information, descriptions, etc… can significantly hurt your sites ability to rank site-wide.
84: Breadcrumb Navigation This is a user-friendly site architecture feature that also helps with on-site linking. Breadcrumbs create a genealogy based link structure that ensures pages that are closer to your homepage will also have more links pointing to them, which reinforces the hierarchy of your site architecture.
85: Mobile Optimized Google has stated sites that are mobile optimized will outrank sites that are not mobile optimized for users on mobile devices. Google’s official recommendation is to use responsive web design rather than to create a separate mobile version of your site. This saves significant time and energy in both building and maintaining a site, while also helping streamline link building and saves bandwidth on Google’s servers.
86: YouTube There is no doubt that YouTube videos are given preferential treatment in the SERPs.
87: Site Usability A site that is difficult to use or navigate can hurt rankings by increasing bounce rate, reducing time on site, reducing pageviews and reducing conversion rate. This may be an algorithmic factor that draws from these various other metrics.
88: Use of Google Analytics and Google Webmaster Tools While Google denies that use of these services will improve a sites rankings in the SERPs, use of these services can certainly help Google fully index a site and provide in depth information in user engagement metrics. Therefore, if a site has good user engagement metrics, then utilizing these services will ensure that those positive signals are fully accessible to Google.
89: Reputation / User Reviews The latest Google quality rater guidelines make it very clear that reputation is a strong ranking factor. While local businesses may understandably not have much of an online reputation because their web presence is fairly small, Google expects to find reputation information on any large business and a webpage cannot be given a high rating if the site has a negative reputation. Reviews and references to a site on local business listing directories like Yelp.com, industry association sites and consumer advocacy sites like RipOffReport.com, play an important role in determine the trustworthiness of a site. These factors likely contribute to a sites ability to rank well. However, reputation information is also strongly influenced by social network engagement and the sentiment of conversations that take place around brand mentions around the web.
The following group of factors is relevant to the backlink profile of both individual pages as well as your entire Domain.
90: Linking Domain Age Backlinks from older domains may pass more trust and authority than links from brand new sites.
91: Quantity of Linking Root Domains The number of referring root domains is one of the most important linking factors.
92: Number of Links From Separate C-Class IPs Links from numerous sites within the same C-Class IP suggests the possibility of a link scheme or link farm. Links from separate class-c IP addresses suggest a more diverse backlink profile.
93: Anchor Text of External Backlinks In notes from Google’s original algorithm it is stated “anchors often provide more accurate descriptions of web pages than the pages themselves.” Therefore, this has always been a strong relevance signal. The idea is that another site is more likely to use anchor text that they feel accurately describes your page, whereas site owners often create descriptions that do not accurately align well with the actual user experience. With Google’s Penguin Update, anchor text was targeted as a factor that may indicate whether your backlink profile is organic or has been build artificially. The idea is that other sites are less likely to use anchor text that is an exact match for the phrase you are actively trying to rank for. Therefore, a backlink profile with too much exact match anchor text can hurt you.
94: Anchor Text of Internal Links Internal anchor text certainly passes relevance signals and allows you to provide Google and site visitors with a signal as to what the page you are linking to is actually about. Google likely weights the anchor text your provide on your site differently than the anchor text used by other sites to link to you.
95: Title Tags for Text Links Title tags associated with text links are a 508 accessibility attribute that give programs for the visually impaired information about the contents and purpose of the link. These signals are also used by search engines as relevance signals.
96: Alt Tag for Image Links Alt tags are a 508 accessibility attribute that give programs that help the visually impaired information about the content of the image. However, search engines can use the content of the image alt tags as a relevance signal. Therefore using keywords in the alt tag can help pages rank for those terms.
97: Links from .edu or .gov Domains Because you typically cannot purchase or manipulate .edu or .gov domains as easily as other TLDs, these sites are believed to hold additional weight in their ability to pass quality signals to search engines. It is generally believed that, all other things being equal, a .edu or .gov link will provide a stronger trust signal than a link from other TLDs.
98: PR of Linking Page The PageRank of the referring page is known to be a very strong algorithmic ranking factor. Links from a higher PR page will pass more “link juice” than links from a lower PR page.
99: Authority of Linking Domain The authority of the linking domain plays a role in the amount of trust that the link will pass. For instance, a link from a featured story on The Huffington Post may pass more trust than a link from a featured story from a lesser known blogger.
100: Links From Competitors in Same SERPs Links from other pages that occupy rankings in the same SERP listings may be more valuable for a page’s ability to rank for that keyword.
101: Social Shares of Referring Page The amount of page-level social shares may influence the value of links on that page. Social shares indicate the popularity of that page, and a link from a more popular and better performing page will provide more trust and authority than a link from a page with little to no social visibility.
102: Links From “Bad Neighborhoods” “Bad Neighborhoods” are networks of sites that are strongly related to spammy, low-quality sites and sites with the type of content that is often banned such as adult content and/or gambling sites. Links from these types of sites can indicate that your site has trust issues and can hurt your rankings.
103: Guest Posts Links coming from guest posts, especially in an author bio area, may not be as valuable as a contextual link on the same page. Also, Google has recently come out stating that the overuse of guest posting as a link building strategy can potentially have a negative SEO impact. To be clear, guest posts on highly relevant and high quality sites is a very good strategy. However, when guest posting crosses the line into low quality posts on arguably unrelated or lower quality blogs, that is when guest posting can become a problem.
104: Links to Homepage Links to your homepage from a referring site may play special importance in evaluating the weight of a link.
105: Nofollow Links This is a controversial SEO topic. Google has stated “in general, we don’t follow them.” Which indicates that the do follow them in some cases. Most SEOs believe that having some percentage of no-follow links in your backlink profile indicates a more natural and organic looking backlink profile.
106: Diversity of Link Types There are many different types of links and if your backlink profile seems to be weighted extremely heavily in favor of some types of backlinks, while other backlin types are being significantly under represented, that could indicate an unnatural link profile and be a red flag that you have engaged in link building schemes that are against Google’s guidelines. The key is to ensure that your backlink profile is appropriately diverse and natural looking. Google wants to reward you for links that other people have decided to give your site, not for links that you built yourself.
107: “Sponsored Links” or Other Words That Indicate Advertising Relationships Words like “Sponsors”, “Link Partners”, “Affiliates”, “Advertising” or “Sponsored Links” that sit relatively close to the links that are pointing to your site from referring pages, indicate that you may have purchased or done something to specifically set up those links and therefore Google will depreciate the value of those links.
108: Contextual Links Links that are embedded within the main written content of a referring page may provide contextual relevance signals and be generally of more value than links that do not appear in close relation to relevant content.
109: Excessive 301 Redirects to Page While 301 redirects have been proven to pass link juice (it is debated whether they pass all or most of the link juice), excessive redirects such as those that go through 3 or more redirects will dilute or even completely drop all link juice. Therefore it is a good idea to evaluate and streamline 301 redirects to avoid any multiple redirect situations. To be clear, it is fine if you have a bunch of pages that have been 301 redirected to point to your page, however you want to avoid situations where a page is redirected to a page that is redirected to a page that is redirected to your page. (See, its even hard to read that type of a mess).
110: Country TLD of Referring Domain Getting links from country-specific domains (eg: .cn, .co, .uk, .in), can help your site rank better in that country.
111: Link Location In Content Links from the beginning of content on a page can carry more weight than links placed at the end of that content.
112: Link Location on Page Where a link appears on a page is important. Links that appear higher on a page or that are embedded in the main body content may carry more weight than links from other placed on the page such as from the comments, sidebar, footer navigation.
113: Relevance of Linking Domain Links from sites that are strongly relevant from within the same niche are more valuable than links from sites that are not as relevant to your focus subject matter. In fact, too many links (or a high percentage of your backlinks) coming from sites that are not relevant to your niche can be a sign of an unnatural backlink profile and participation in link schemes, which is a violation of Googles guidelines and can result in penalties against your site.
114: Relevance of Linking Page Often you may get links from sites that are not necessarily focused on your niche subject matter as a whole, but do features relevant sections. For instance a news site or consumer reports type of site may be general in nature, but getting links from a page that is relevant to your niche subject matter is better than getting links from an unrelated page.
115: Sentiment of Text Around Link Google is very focused on semantics for the purpose of natural language recognition and searching for sentiment signals. Voice search through the Android platform is a major driver of this, and a byproduct is an improved ability to understand whether a link to your site is being used in a positive or negative context. It is believed that links from discussion that express a positive view of your page/site/brand carry more weight than links that are associated with negative sentiment.
116: Keyword in Title If a page that is linking to you is using your target keyword in the title of that page, this will cause that link to carry additional link juice.
117: Positive Link Velocity A site with positive link velocity, meaning that it is gaining in the quantity of backlinks (think of an upward trending graph), will get a boost in the SERPs.
118: Negative Link Velocity If a site is quickly loosing links it indicates that its link partners are abandoning that site and this may indicate a deeper problem. Therefore this is a signal that can hurt the rankings of a site.
119: Links from HUB pages Getting links from pages that are top resources on your target subject matter can give your site a boost in ranking for relevant search terms.
120: Links from Authority Sites A link from a highly authoritative site will pass more link juice than a link from a less authoritative site.
121: Linked To as a Wikipedia Source While these are no-follow links, it is widely believed that links from Wikipedia send powerful trust signals.
122: Co-Occurrences The words that tend to appear around backlinks to your site from numerous referring pages send relevance signals to Google.
123: Co-Citation When your site is consistently mentioned by pages that are discussing your subject matter, regardless of whether those pages are actually linking to your site, that is a relevance signal that can positively affect your TrustRank. This is difficult to establish for sites that do not have a particularly strong brand, however for strongly branded sites this can provide a boost to rankings.
124: Backlink Age According to a patent filed by Google, older backlinks pass more link juice than new links.
125: Natural Link Profile A site with a backlink profile that appears “natural” will rank more highly and be more durable to algorithm updates. This means that if the links seem like they were developed organically rather than purposely built by the owner of the site, you will rank higher. Also, if your sites backlink profile seems like it was purposely built for the purposes of manipulating the SERPs, then that is explicitly against Google’s guidelines and your site could be subjected to a manual penalty.
126: Reciprocal Links Reciprocal links are when a site links to you and you link back to that site. It is natural for websites to participate in some reciprocal linking, however Google’s Link Schemes page states that “excessive link exchanging” is a considered a link scheme and should be avoided.
127: User Generated Content LInks Google is able to identify links generated through user generated content rather than by the owner of the site. Therefore, if you set up a profile on a site or contribute content with links such as in comment links, Google will not allow those links to pass as much link juice as links created by the site owner.
128: Link Juice Passed Through 301 Redirects Links from 301 redirects may lose a little bit of link juice, however Google has stated and numerous tests have provedn that 301 redirects do pass the link juice from the redirected page to the target page.
129: Schema.org Microformats / Rich Snippets Pages that offer structured data through microformats have an advantage over pages that do not feature such structured data. Whether this is a direct boost, or an indirect benefit due to rich snippets improving click through rate on SERPs is debatable. Likely both are contributing factors. However, it is known that structured data directly contributes to Google’s knowledge graph and knowledge graph is becoming an increasingly important component of the services offered by Google. Therefore, structured data is incredibly important.
130: DMOZ Listed Is is widely believed that Google gives a little extra trust to sites that are listed in the DMOZ directory.
131: Yahoo! Directory Listed Because the Yahoo! directory has been cataloging sites for such a long time and has categorized the web so extensively, it is believed that Google gives some weight to sites that are featured in the Yahoo! directory.
132: Number of Outbound Links on Page Each page has a certain amount of link juice that it can pass. A page that features 100 outbound links has its link juice divided among those 100 links, whereas a page with 20 links is only dividing its link juice among those 20 links. However, this consideration is independent of the PageRank, TrustRank, Authority and Relevance of the page. Therefore, a link from an extremely high quality page that also has 100 outbound links, is likely worth more than a link from a low quality page with only 20 outbound links.
133: Forum & Social Profile Links Because link spamming is so widespread, it is believed that Google significantly devalues links from forum profile pages.
134: Word Count of Content on Linking Page If the authority and relevance considerations are equal, a link from a page with 800 words of content is likely to be better than a link from a page with only 75 words of content.
135: Quality of Linking Content Links from content that is poorly written content that contains spelling or grammatical errors and does not offer an in depth exploration of the subject matter, is worth much less than a link form a page with a high quality, well written in-depth exploration of the subject matter.
136: Sitewide Links Google compresses sitewide links to count as a single link. However, if sitewide links are account for a significant percentage of your backlink profile, then your site could be flagged for a link scheme.
The following group of factors tracks user interaction metrics with individual pages, your site on the whole and the homepage of your site could possibly be seen as uniquely relevant. User engagement metrics can provide Google with insights into the quality of your site from a user perspective.
137: Organic Click Through Rate for a Keyword Pages that get clicked more for a particular keyword will get pushed up in the SERPs for that keyword.
138: Organic CTR for All Keywords A high CTR for a page/site will help that page/site consistently rank higher for relevant keywords.
139: Bounce Rate & Dwell time A high bounce rate indicates that your site is not delivering the expected user experience and therefore your site may not deserve to rank highly for the keyword that generated that click. Similarly, a very low bounce rate indicates that users are satisfied with the user experience your site offers and thereby give your site a boost in the rankings. Google has denied using bounce rate as a ranking factor, however Dwell time is specifically referred to in Google content quality patent as a metric considered in determining a webpages quality score. Dwell time is the amount of time it takes for a user to return to Google after having clicked on a search result. When a user clicks on your link from Google's search results, the amount of time they take before returning to Google is the Dwell time. A longer Dwell time indicates that they have been engaged in information that they enjoyed and this indicates a high quality page.
140: Direct Traffic Google uses data gathered both through the Google Chrome browser and possibly from Google Analytics to monitor the amount of direct traffic a site receives. Significant amounts of direct traffic are an indicator of a high quality site and these trust signals can help a site rank higher in SERPs.
141: Repeat Traffic Google may give positive consideration to sites with significant repeat traffic. A high visitor return rate may give your site a boost in the SERPs.
142: Bookmarks Sites that get bookmarked by users may get a boost as this is a positive user experience and trust signal. Google can see bookmarks in the Chrome Browser and also indexes popular bookmarking sites like Delicious.
143: Google Toolbar Data It has been reported by some SEOs that Google uses toolbar data for page loading speed and malware reporting.
144: Number of Comments Pages that generate a lot of comments, that are on topic as opposed to spammy, indicate user engagement and will tend to rank higher in the SERPs.
145: Time on Site Google analytics and the Chrome Browser can both report time on site to Google. it is believed that time on site is used as an indicator of user engagement and therefore sites with higher time on site can be expected to receive a rankings boost.
The following factors may only be significant under special circumstances.
146: Query Deserves Freshness Some searches indicate that the user is looking for information where freshness is key. These types of searches go into a query bucket that takes freshness into heavier consideration. In these instances a newer page may have an advantage over an older page. At the very least, this is an instance where page update frequency is important. If an older page consistently shows that it is always kept up to date, then it will have an advantage over the newer pages.
147: Query Deserves Diversity If the keyword being searched is fairly ambiguous and does not clearly indicate the user intent, then Google may opt to provide greater diversity in the types of results being delivered.
148: User Browsing History Sites that you frequently visit while signed into Google get a bump in SERPs for your searches.
149: User Search History The chain of searches that you use during a session will influence the types of results that you receive. For instance, if you search “running accessories” and then your next search is “shoes” Google is more likely to return results that feature running shoes in your second search.
150: Geo Targeting Google gives preference to sites with a local server IP and country-specific domain name extension.
151: Safe Search Search results with curse words or adult content won’t appear for people with safe search turned on.
152: Google+ Circles When you are signed into Google. Google shows higher results for authors and sites that you have in your Google+ circles and for people who are in the circles of the people that you have in their circles. These social results can be turned on or off when you are signed in to Google.
153: DMCA Complaints Google penalizes pages with DMCA complaints for copyright infringement.
154: Domain Diversity The Google Bigfoot Update focused on ensuring that a single domain could not dominate a single SERP page, and therefore added a greater diversity of domains to search results.
155: Transactional Searches Search queries that demonstrate transactional user intent such as “buy shoes” or “find flights” will trigger Google search results that cater to pages that offer suitable transactional type content and functionality.
156: Local Searches Search queries that contain terms for the types of services that are strongly associated with intent to interact with a local business will return search results that feature local business listings and a map featuring local businesses fitting the category. These SERPs are the result of a specialized local algorithm that features Google+ Local Pages listings.
157: Google News Box Certain search queries are placed into a query bucket that will trigger a Google news box, featuring the latest Google news stories that are relevant to the query.
158: Big Brand Preference The Google Vince Update began delivering search results that gave big brands a boost for certain general search queries.
159: Shopping Results Some searches are placed into a query bucket that triggers Google shopping results in organic SERPs. Google shopping results are taken from the Google Products service, which was once a free service offered by Google but is now a paid advertising comparison-shopping engine.
160: Image Results For search queries that are commonly used on Google Image Search, Google will display an image result box within the organic SERP.
161: Site Links Branded search queries can trigger results that display site links. This is where Google will typically feature the homepage of the site at the top of the search results, and then feature up to six additional links to deeper pages within that site. This type of result is very dominating and powerful and is only supposed to be delivered for strongly brand related keywords. The site links that Google will display typically represent the most important and popular pages on your website, so while you cannot tell Google which pages to display as site links, you can establish which pages are the most important through the XML Sitemap and using internal links, and you can attempt to drive traffic to specific pages within your site through a well crafted user experience. However, if Google is showing certain site links that you do not want displayed, then you can go into Google Webmaster tools and tell Google to stop displaying those site links.
Social signal provide Google a human curation of the web and therefore are being used to help Google understand who is interacting with your site and whether the user experience was positive or negative. Positive Social engagement metrics are strongly correlated to high search engine rankings.
162: Number of Tweets Like links, the number of times a site or page has been tweeted is a strong social trust and quality signal.
163: Authority of Twitter Users Accounts It is believed that tweets that come from Twitter user accounts that have more followers, carry more weight than accounts with a small number of followers. For instance, if Justin Bieber tweets about your business it may help you more than if your mom does. (No offense to your mom)
164: Number of Facebook Likes Although Google denies it, there has been several studies that demonstrate evidence that pages with a lot of Facebook likes will get a boost in rankings. Again, this is a social trust signal that makes sense.
165: Facebook Shares Facebook shares, because they are effectively a social backlink, may provide a stronger boost than Facebook likes.
166: Authority of Facebook User Accounts Similar to Twitter, likes and shares from more popular Facebook users and pages may pass more weight than those from less popular accounts.
167: Pinterest Pins Pinterest is one of the most popular social networks online and is more like a bookmarking service than Twitter or Facebook, therefore it could provide Google both social trust signals and help to demonstrate category relevance.
168: Votes on Social Sharing Sites It is believed that Google uses shares at sites like Reddit, StumbleUpon and Digg as another type of social quality and trust signal.
169: Number of Google+ 1’s Google has denied using Google+ for ranking signals, however various test by independent SEOs have shown that when a new page is given a bunch of Google+ 1’s, it’s rankings improve. Coincidence? We think not. Google+ is important and many SEOs believe that it is by far the most important of the social networks because of its potential to influence search rankings.
170: Authority of Google+ User Accounts It just makes sense that Google would weight +1’s coming from more authoritative accounts more heavily than those from less popular accounts.
171: Verified Google+ Publisher & Author Social Profiles In February 2013 Google CEO Eric Schmidt said “Within search results, information tied to verified online profiles will be ranked higher than content without such verification”… but Eric… you don’t use Google+ signals… remember? Actually in the leaked 2014 Google quality rater program guidelines, authority of the author of a page is a consistent theme and necessary component of what Google considers a high quality page. However, Google has also discontinued support for the Google+ Author Content relationship. Apparently, these authority signals are now being aggregated from all social profiles that can be traces to an author, and/or publisher.
172: Authorship History With the introduction of Google+ Authoriship mark-up Google began tracking the history of authors just as they always have with websites. Authors who consistently create high quality content on a specific subject matter will see that, over time their articles will achieve higher search rankings more quickly due to their legacy of authority on that subject matter. This is true, independent of the sites where the content actually appears. Therefore, if an author changes jobs, or begins writing for a new site, their authorship history and authority is carried over with them.
173: Publisher History The above is also true for domains. Whereas authorship markup help Google track the history of relevance, quality, authority and popularity of authors, Publisher markup does the same for domains.
174: Social Signal Relevancy It is believed Google uses relevancy information from the account sharing the content and the text surrounding the link. Therefore if someone who is an expert on the subject matter says something good about your content when they share that, it will be weighted more heavily than if someone less authoritative on the subject matter shares it. And if they say something bad about your content, that could also send negative signals.
175: Site Level Social Signals If you site gets a lot of social shares it will reflect better on your site as a whole, demonstrating user engagement, and could give you a boost in the rankings.
Google clearly gives positive treatment to recognized brands. However, not all websites are considered credible brands. The following factors can be used by Google to determine the legitimacy of a brand. These factors will tend to influence the TrustRank of a site.
176: Brand Name Anchor Text Branded anchor text is a simple but strong brand signal that can help your site improve it’s rankings overall.
177: Branded Searches When people begin searching more and more for your brand name, that sends strong brand signals to Google. It demonstrates trust, quality, user engagement and will give your site a significant boost in SERPs.
178: Facebook Page Likes Brands tend to have Facebook pages with lots of likes. This is a strong brand signal to send Google.
179: Twitter Profile Followers If your brand has its own Twitter profile with lots of followers that is a strong brand signal to send Google.
180: LinkedIn Company Page A LinkedIn Company Page can provide a strong brand signal. Your company page should be well optimized, including links to the most important category pages on your site, and should be promoted to effectively attract a lot of followers.
181: Employees Listed at LinkedIn It has been speculated that your employees having LinkedIn profiles that say they work at your company can send a brand signal.
182: Legitimacy of Social Media Accounts Fraudulent social accounts and buying of social followers is a problem. However, a strong and legitimate social media account can send very strong and positive brand signals. For instance, a social account with 20,000 followers and just a few posts sends a very different signal than a social account with 20,000 followers and a long history of posts and interactions.
183: Brand Mentions on News Sites Established and legitimate brands tend to get mentioned in the media. Therefore, news stories that mention (co-citation) your brand and link to your site will be strong indicators of brand legitimacy.
184: Co-Citation Brands get mentioned even when they are not linked to. If people tend to mention your brand when they talk about the subject matter you are relevant to, that can send a strong signal that your brand is an important player in that space. This can provide a significant boost to your sites ability to rank highly.
185: Brick and Mortar Location With Google+ Local Listing Real businesses tend to have offices and it is certainly possible that Google utilizes it’s Google+ Pages data to verify the legitimacy of a business.
186: Website is a Tax Paying Business It has been postulated that Google looks as to whether a site is associated with a tax paying business.
The following group of on site factors are strongly correlated with search engine penalties for strategies that Google has classified as web spam.
187: Panda Penalty Sites with low quality content, aggregated content, thin content, spun content, error filled content, content that does not seem to provide an in-depth exploration of the subject matter, were hit hard after the Panda Update (and successive iterations) in favor of sites with high quality content.
188: Links To Bad Neighborhoods Linking out to “Bad Neighborhoods” such as content farms, adult content, thin affiliate sites, etc… can significantly hurt the credibility of your site and thus hurt your search rankings.
189: Redirect Doorway Pages Redirecting through doorway pages is a violation of Google guidelines and can get your site penalized or de-indexed.
190: Over Use Of Advertising On A Page The Google Page Layout update introduced penalties for pages that feature ads too prominently, or are distracting from the main content of the page. Ads above the fold are OK, but if you use more than one or two above the fold you could be asking for trouble. In the most recently leaked Google quality rater guidelines, Google clearly indicates that pages featuring ads that are formatted to look like supplementary content, or pages that break up the page content with multiple ads are jarring to the user experience at best and deceptive at worst. The Google quality rater guidelines clearly state that these tactics are reason enough to downgrade the quality of a page.
191: Site/Page Over Optimization The over use of elements that could potentially have a positive effect on your site can actually hurt you. It’s like the old saying, “too much of a good thing, can be a bad thing”. This includes things like “keyword stuffing” which leads to keyword densities that exceed 7%, “header tag stuffing” where you overuse header tag elements with target keywords or over use of your exact keyword in the important on-page SEO elements such as 508 accessibility attributes.
192: Hiding Affiliate Links If you try to hide affiliate links through tactics such as cloaking, your site could be penalized.
193: Affiliate Site Google isn’t a big fan of affiliate sites because they tend to lead people down the road of spammy strategies. It is fine to be participate in affiliate relationships, however affiliate sites are believed to be placed under additional scrutiny. Therefore, it is highly advised that any affiliate activity is clearly in compliance with Google guidelines.
194: Auto-Generated Content If your site is auto-generating content, it could get you penalized or de-indexed. Also, that type of content tends to be very low quality and typically does not offer a good user experience.
195: Excessive PageRank Sculpting If your site puts a lot of effort into PageRank sculpting through no following all outbound links it may be a sign of gaming the system. While this may not result in a direct penalty, it could bring your site under the increased scrutiny of the Google quality rater program.
196: IP Address Flagged As Spam If an IP address is flagged for spam it may hurt all of the sites on that server. This is why shared hosting could result in your site getting penalties that you are not even aware of.
197: Meta Tag Spamming If you are using meta tags to overstuff keywords, that is something that Google can see very quickly. Remember that Google is getting very good at understanding language. You want to use keywords in your meta tags, but a list of keywords could signal a problem and hurt your site.
The following group of off site factors are strongly correlated with search engine penalties for strategies that Google has classified as web spam.
198: Unnatural Influx of Links A sudden influx of links, particular of a specific type of link or from a specific type of site can indicate to Google that you are building links and result in a penalty. Of course, you could be running a contest, promotion or just released a new product, which would be perfectly acceptable and would actually help your rankings. However, if you are all of the sudden generating an unusual amount of comment links, directory links, or optimized links from syndicated content, that is the sign of a problem. Any spike in links is a bit suspicious. It is better to build links consistently over time.
199: Penguin Penalty Sites that were hit by the Google Penguin penalty are significantly less visible in search.
200: Link Profile with High % of Low Quality Links Lots of links from sources commonly used by black hat SEOs, such as comment and forum links, is a signal that you are using low quality link building strategies. Some of these types of links may be perfectly acceptable, however they must be balanced with lots of higher quality link signals as well.
201: Linking Domain Relevancy If your backlink profile is dominated by links from sites that are contextually relevant to your niche, then you will get a nice boost, however, if your backlink profile is dominated by links from unrelated sites then that could be a problem and get your site penalized.
202: Unnatural Links Warning Google has sent out thousands of notices in Webmaster Tools saying that they have detected unnatural links. Sites that have received this message have experienced a significant drop in rankings (although not 100% of the time).
203: Links From The Same Class-C IP Getting an unusual number of links from sites that are on the same C-Class IP is a sign of participation in a link farm.
204: Poison Anchor Text Some specific keywords, particularly pharmaceutical related terms, as anchor text of links pointing to your site is a sign that your site may have been hacked or is participating in phishing, malware or other bad practices. These signals could get your site banned from Google.
205: Manual Penalty If Google quality raters have found that your site is in violation of the Google guidelines, they could place a manual penalty on your site and remove your site from the SERPs.
206: Selling Links Selling links is explicitly against Google’s guidelines and can cause your site to be penalized and deindexed.
207: Google Sandbox New sites that suddenly get a massive wave of new links are sometimes placed in the Google sandbox which temporarily limits search visibility while a Google quality rater assesses the situation.
208: Disavow Tool In cases where sites may be penalized for certain links, Google asks that the webmaster first contact the owner of the site to have the bad links taken down and if that does not work then the webmaster may use the disavow tool to inform Google that those links should not be associated with the backlink profile of the site.
209: Reconsideration Request If a site has experienced a manual penalty and has corrected the situation, then the webmaster may submit a reconsideration request asking Google to lift any manual penalty and return to the rankings.
Importance of Algorithm Ranking Factors
The following chart is based upon feedback from a survey of 128 respected SEO professionals. The survey was conducted by Moz.com in late 2013. Therefore, while the following chart of ranking factors may not actually represent the weighting of these factors by Google, it is the result of a consensus of a significant number of people with experience implementing SEO strategies.